To fully grasp the concept of Metro Ethernet, it’s essential to understand its underlying framework—the Metro Ethernet network architecture.
Metro Ethernet is a high-speed data transport network that utilizes the Ethernet standard to efficiently interconnect multiple customer sites within a metropolitan area.
Acting as an intermediate solution, Metro Ethernet bridges the gap between Local Area Networks (LANs), which cover a single building or campus, and Wide Area Networks (WANs), which encompass larger geographical areas, including multiple cities or countries.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects of the Metro Ethernet network architecture and its implementation in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs).
We will not go deep into an explanation of Metro Ethernet in this post, as we already have a post that explains Metro Ethernet in detail.
Metro Ethernet Network Architecture
Metro Ethernet Network architecture can take two forms: Full mesh topology and Hub-and-Spoke topology. Each of them has a different topological arrangement.
Full Mesh Topology For Metro Ethernet Network
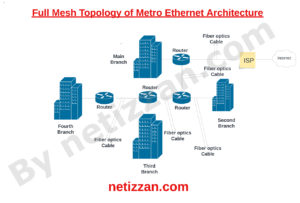
In a Full Mesh Topology, each customer edge router is directly connected to another customer edge router, forming a fully interconnected network.
As you can see from the topology above, there is a dedicated point-to-point Ethernet link between each routers. This connection is done using Fiber optics cables.
Here are key components of the Full Mesh Topology shown above:
1) Ethernet Source: This is the central network that provides the Metro Ethernet service to the customer. In the topology above, ISP is the Ethernet source that is serving the whole branches.
2) Customer Edge Routers: These are routers located at each branch offices and it is helps in exchanging traffic between the branch’s LAN to the Customer’s WAN.
3) Branch Offices: Represent the various locations of the customers that are part of the Metropolitan Area Network. Each branch office has its own customer edge router (CE router) to connect its local devices to the Metro Ethernet WAN.
4) Fiber Optic Cables: It is used to establish high-speed and reliable connections between one customer edge routers to another.
Hub-and-Spoke Topology For Metro Ethernet network
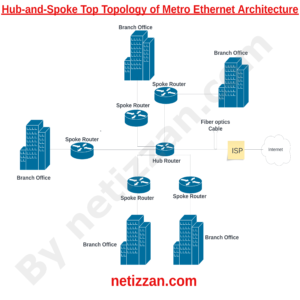
In a Hub-and-spoke Topology, a central router known as Hub router is giving link to every other routers in the network.
As labeled in the topology above, the central router is Hub Router while every other routers connecting to it is Spoke router.
The spoke routers in this topology is serving as the customer Edge routers which is the gateway for each of the branch’s Local Area network.
Here are key components of the Hub-and-Spoke Topology shown above:
1) Ethernet Source: This is the central network that provides the Metro Ethernet service to the customer. In the topology above, ISP is the Ethernet source that is serving the whole branches.
2) Hub Router: This is the central router that is providing link to every other Routers in the network. It is directly connected to the ethernet source.
3) Spoke Routers: This is the Router at the customer’s Edge. It is serving as the gateway for Each of the Branch’s LAN.
4) Branch Offices: These are the various locations of the organization’s branch that are part of the Metropolitan Area Network.
Each branch office has its own customer Spoke router to connect its local devices to the Metro Ethernet WAN.
5) Fiber Optic Cables: It is used to establish high-speed and reliable connections between one customer edge routers to another.
Metro Ethernet Architecture Vs. Carrier Ethernet Architecture
Metro ethernet has the same network architecture with Carrier ethernet for both Full mesh topology and Hub-and-spoke Topology except that Carrier Ethernet Architecture has higher number of branches and Cover larger geographical areas.
Conclusion
From what we have covered, you have seen the architectural view of Metro Ethernet. Metro Ethernet uses the Ethernet standard to provide connectivity to a metropolitan area, which is usually less than a city but way more than a home or branch office.

I am a passionate Networking Associate specializing in Telecommunications.
With a degree in Electronic engineering, I possess a strong understanding of electronic systems and the intricacies of telecommunications networks. I gained practical experience and valuable insights working for a prominent telecommunications company.
Additionally, I hold certifications in networking, which have solidified my expertise in network architecture, protocols, and optimization.
Through my writing skills, I aim to provide accurate and valuable knowledge in the networking field.
Connect with me on social media using the links below for more insights.
You can contact me using [email protected] or connect with me using any of the social media account linked below


