In today’s interconnected world, reliable and high-speed networking solutions are essential for businesses to thrive. One solution to this that has gained significant popularity is Metro Ethernet.
Metro Ethernet covers a larger geographic area than LAN, it is a type of WAN technology specifically designed for metropolitan areas.
In this article, we will explore the concept of Metro Ethernet, its services, architecture, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is Metro Ethernet?
Metro Ethernet is an Ethernet transport network that utilizes Ethernet standards to provide high-speed data transmission within a metropolitan area. It offers businesses a cost-effective and scalable solution for connecting multiple locations within a city or metropolitan region.
Metro Ethernet, also referred to as a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) utilizes pure Layer 2 connectivity to provide various types of services within a metropolitan area. It offers point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multipoint-to-multipoint connectivity options.
Metro Ethernet is commonly used by businesses, organizations, and service providers to establish high-speed, scalable, and cost-effective network connections between multiple customer sites within a metropolitan region.
Metro Ethernet Services and Topologies
Metro Ethernet services encompass a range of connectivity options tailored to meet the wide needs of Enterprises. Some common services include Ethernet Line Services, Ethernet LAN Service, and Ethernet Tree Service.
1) E-Line (Ethernet Line Service):
E-Line, also known as Ethernet Private Line or Ethernet Virtual Private Line, is a Metro Ethernet service that emulates a dedicated point-to-point Ethernet connection between two locations. It is designed to provide secure and reliable communication between specific endpoints.
E-Line offers a simple and cost-effective solution for organizations that require direct, high-bandwidth connectivity between their sites.
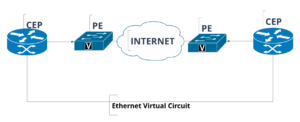
E-Line involves two Customer Ethernet Ports (CEPs), which are connected by a Provider Ethernet Port (PE). The PE acts as a bridge, ensuring that the Ethernet frames transmitted between the CEPs are encapsulated and securely delivered over the Metro Ethernet network.
2) E-LAN (Ethernet LAN Service):
E-LAN, also referred to as Ethernet Multipoint Service or Ethernet Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS), is a Metro Ethernet service that enables communication between multiple locations as if they were connected to the same Local Area Network (LAN). It provides a flexible and scalable solution for businesses with multiple sites that need to share data.
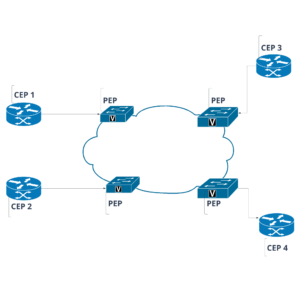
E-LAN involves multiple CEPs connected to a PEP. The PEP functions as a central hub or bridge, allowing Ethernet frames to be distributed among the various CEPs. This architecture creates a multipoint connectivity model, where data can be transmitted between any combination of connected locations.
3) E-Tree (Ethernet Tree Service):
E-Tree is a Metro Ethernet service that enables point-to-multipoint communication, used in scenarios where a centralized site needs to communicate with multiple remote locations. It is ideal for businesses that require a hierarchical network topology, such as educational institutions, where data distribution needs to be controlled from a central point.
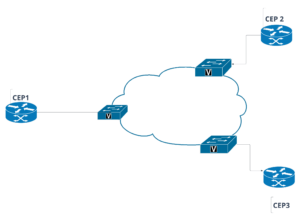
E-Tree is based on a root-spoke model. It consists of a root CEP(CEP1), representing the central site, and multiple leaf CEPs (CEP2 & CEP3), representing the remote locations. The root CEP acts as the central hub, while the leaf CEPs serve as the endpoints that receive data from the root.
Metro Ethernet Architecture
The Metro Ethernet architecture consists of several components that ensure efficient data transmission and network management. These components include customer premises equipment (CPE), provider edge (PE) components, and metropolitan area network (Metro Ethernet).
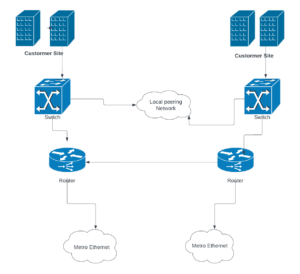
- Customer Premises Equipment (CPE): CPE refers to the networking devices or equipment located at the customer’s premises. This can include routers, switches, or other devices that connect the customer’s local network to the Metro Ethernet service. CPE is represented as customer’s site in the Diagram above.
- Provider Edge (PE) Component: PE components serve as the boundary between the customer’s network (Customer’s site) and the service provider’s network(metro ethernet). They are responsible for connecting the customer’s CPE to the Metro Ethernet service and play a crucial role in ensuring secure and efficient data transmission. In the diagram above, PE is a combination of the router & switch at the center.
- Metropolitan Area Network (Metro Ethernet): Metropolitan Area Network is a vital part of the Metro Ethernet architecture. They enable connectivity within the provider’s network and facilitate the transfer of data between different customer locations. MAN are responsible for handling traffic, implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies, and ensuring efficient delivery of Metro Ethernet services.
Metro Ethernet Standard
The Metro Ethernet standard is defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.3 standard. The standards is tabulated below:
| Name | Speed | Distance |
|---|---|---|
| 100Base-LX10 | 10 Km | 100 Mbps |
| 1000Base-LX | 5 Km | 1 Gbps |
| 1000Base-LX10 | 10 Km | 1 Gbps |
| 1000Base-ZX | 100 Km | 1 Gbps |
| 10Gbase-LR | 10 Km | 10 Gbps |
| 10Gbase-ER | 40 Km | 10 Gbps |
| 40Gbase-LR4 | 10 Km | 40 Gbps |
| 100Gbase-ER4 | 40 Km | 100 Gbps |
Emerging Technologies in Metro Ethernet
The Metro Ethernet landscape is constantly evolving to meet the increasing demand for high-speed connectivity. Some emerging technology include:
- Adoption of Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN is a network architecture that separates the control plane and data plane of a network. SDN allows for centralized control and management of network resources, enabling more efficient provisioning, configuration, and management of Metro Ethernet services. SDN can enhance the flexibility, scalability, and agility of Metro Ethernet networks by dynamically adjusting network configurations and policies.
- Integration of Metro Ethernet with cloud computing: Metro Ethernet can be integrated with cloud computing to create a comprehensive and interconnected ecosystem. This integration allows for efficient and scalable access to cloud resources over Metro Ethernet connections.
- Integration of Metro Ethernet with IoT: Integrating Metro Ethernet with the IoT enables reliable and high-speed connectivity for IoT devices within a metropolitan area, supporting the exchange of data and enabling smart city initiatives, industrial automation, and various IoT applications.
- DWDM Technology: Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is a fiber-optic transmission technique that combines multiple wavelength signals onto a single fiber, allowing for increased bandwidth and extended transmission distance in optical networks.
- Demux: DWDM multiplexers and demultiplexers are core optical multiplexing technologies that enable the transmission of data from various sources on different light wavelengths. They help extend the bandwidth of optical networks with low cost and long transmission distances.
- Optical Amplifiers: Optical amplifiers compensate for signal losses caused by fiber attenuation, power splitting, and other factors. Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) are commonly used in DWDM applications due to their ability to provide small signal gains and output powers.
- Coherent Optical Technology: Coherent optics, particularly small pluggable CFP2 and CFP4 modules, have gained attention and adoption in metro networks. Coherent optics leverage technologies such as higher-order modulation and coherent detection to optimize performance and size.
Applications of Metro Ethernet
Metro Ethernet finds applications in various industries and sectors. Metro Ethernet:
- Enables efficient data transfer for businesses with multiple branches,
- Connect Business to the internet,
- Facilitates video conferencing and collaboration tools that requires multi-cast delivery
- Supports cloud connectivity,
- Serves as a backbone for Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in delivering broadband services.
Benefits of Metro Ethernet
Metro Ethernet offers several advantages over traditional networking solutions. Viz
- High Bandwidth services: Metro Ethernet network has a high bandwidth capacity that enhances high-speed transmission,
- Scalability: Metro Ethernet Network allows you to easily integrate new branches into the network
- Flexibility:
- Flexibility: The Metro Ethernet network allows organizations to easily adapt to changing business needs.
- Low latency: No delay in transporting frame from source to Destination
- Network security.
- Cost-effectiveness.
Limitations of Metro Ethernet
While Metro Ethernet offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consider its limitations. Below are some of the limitations:
1) Dependency on the service provider’s network infrastructure: If there are issues or outages in the provider’s network, it can impact the connectivity and performance of Metro Ethernet services.
2) Metro Ethernet may not be available in all geographical locations, limiting its accessibility for businesses operating in certain areas.
3) Quality of Service (QoS) Limitations: Ensuring consistent QoS can be challenging in a shared Metro Ethernet environment
4) Reliability Challenges: Metro Ethernet networks rely on physical infrastructure, such as fiber optic cables or copper lines, which are susceptible to damage from natural disasters, construction activities, or other external factors.
Conclusion
Metro Ethernet is an Ethernet transport network that utilizes Ethernet standards to provide high-speed data transmission within a metropolitan area. It offers many advantages to businesses by providing cost-effective and scalable connectivity.
With what we have covered so far, you have learned the core concept of Metro Ethernet and have also seen the benefits and limitations of this technology. You would do well to leave your question in the comment section.

I am a passionate Networking Associate specializing in Telecommunications.
With a degree in Electronic engineering, I possess a strong understanding of electronic systems and the intricacies of telecommunications networks. I gained practical experience and valuable insights working for a prominent telecommunications company.
Additionally, I hold certifications in networking, which have solidified my expertise in network architecture, protocols, and optimization.
Through my writing skills, I aim to provide accurate and valuable knowledge in the networking field.
Connect with me on social media using the links below for more insights.
You can contact me using [email protected] or connect with me using any of the social media account linked below



Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles
as long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My blog site is in the very same niche as yours and my users would really benefit from some of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Many thanks!
You can quote it as long as you credit us back, and it should be on Fair use cases.
I blog quite often and I truly appreciate your content.
Your article has really peaked my interest.
I will bookmark your website and keep checking for new details
about once a week. I subscribed to your Feed too.
Thanks for the complement. We will keep updating new content. Keep checking!
Good information. Lucky me I came across your website by chance (stumbleupon).
I’ve bookmarked it for later!