Enterprise customers of different ISPs usually have their branches dispersed across different geographical locations. This enterprise needs to interconnect each of their branch offices using their Wide Area network. This reduces cost, enhance secure communication, and ensure good management.
However, Procuring the equipment needed to interconnect these branches is not cost-effective for enterprises. So, ISPs usually lease their own internet line running from the enterprise’s main branch to the destination branch where they want to extend the internet.
In this article, we will walk you through the leased line network architecture so that you have an idea of how the connection is run. We will not go deep into an explanation of leased lines in this post, as we already have a post that explains leased lines in detail.
Leased Line Connection Diagram
Below is a block diagram illustrating a typical leased line network architecture connecting two branch offices (Branch A and Branch B) to the internet through an ISP network.
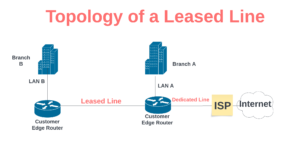
In this diagram,
-
Branch A and Branch B Represent two geographically separated branch offices. Each office hosts a local area network (LAN) consisting of computers, servers, and other devices used for day-to-day operations.
-
Router A and Router B: These routers serve as the vital communication nodes between the two branch offices. They are responsible for establishing and managing the leased line connections, ensuring secure data transfer between Branch A and Branch B.
-
Leased Line Connection: The line between the two routers indicate the leased line connections. This dedicated connection ensures that data flows directly and exclusively between the two offices.
-
ISP Network: The leased line extends beyond Router A and connects to an ISP network. The ISP network is the gateway to the global internet, providing access to various online services and resources.
-
Cloud (Internet): The ISP network further connects to the cloud, representing the vast ecosystem of cloud service providers and web-based applications. This direct connection to the cloud enables the branch offices to access cloud resources with speed and reliability.
Conclusion
From what we have covered, you have seen that a leased line is just a point-to-point connection between an organization’s branch they obtained internet with and their other branch. This point-to-point connection consisted of two routers placed at each of the branches, and a cable connected each router.
This connection helps the organization save money by extending the WAN to their other branches rather than having to pay another ISP provider for each of their branches.

I am a passionate Networking Associate specializing in Telecommunications.
With a degree in Electronic engineering, I possess a strong understanding of electronic systems and the intricacies of telecommunications networks. I gained practical experience and valuable insights working for a prominent telecommunications company.
Additionally, I hold certifications in networking, which have solidified my expertise in network architecture, protocols, and optimization.
Through my writing skills, I aim to provide accurate and valuable knowledge in the networking field.
Connect with me on social media using the links below for more insights.
You can contact me using [email protected] or connect with me using any of the social media account linked below


