Leased Line and Dedicated Line are two connectivity technologies that can be confusing concepts due to their close relationship, but they have distinct differences that are worth researching. While both technologies are used for extending wide area networks(WAN) to distant locations, their major differences lie in their use cases.
In this article, we will delve into leased lines vs. dedicated lines, examining what they are, how they are related, and how they differ in their respective use cases.
What is a Leased line?
A leased line is a dedicated point-to-point connection between two local area networks. It is commonly used to extend an organization’s wide area network (WAN) from one location to another.
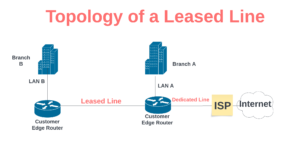
Leased line provides a high-bandwidth, secure interconnection between branches, ensuring privacy and exclusivity for the organization’s use. Organizations can obtain leased line from their internet service provider or other ISPs that have coverage between their main branch and the branch at which they want to extend their LAN to.
The primary aim behind leasing a line is that instead of establishing and maintaining their own link to connect branches, organizations opt to rent an existing network channel and pay a fee. This approach offers significant cost savings by eliminating the need to invest in expensive equipment.
Leased lines can be either dedicated or shared channels. A dedicated leased line is exclusively used by a single organization, providing unmetered bandwidth and a high service level agreement since there is no sharing of the channel with other parties.
On the other hand, a leased line is shared when multiple organizations utilize the same channel to extend their wide area networks(WAN) from a branch near their ISP to other branches situated at different locations.
One key feature of leased lines is that they provide symmetrical bandwidth, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same. This symmetrical nature is beneficial for organizations that require fast and consistent data transfer in both directions, such as companies with substantial data backup and synchronization needs or those running real-time applications.
Recommended: Leased line Network Architecture
What is a Dedicated Line?
A dedicated line is a point-to-point connection that is exclusively dedicated to a single purpose or service.
Unlike leased lines, which can be shared channels, Dedicated lines are not shared; they are used to provide dedicated internet access to enterprise businesses to enhance high bandwidth, secure communication, and a higher service level agreement.

Dedicated lines can be established using various technologies, including leased lines, or virtual private networks (VPNs).
Unlike leased lines, dedicated lines are not limited to connecting specific geographic locations. They can also be used to establish direct connections to cloud service providers, internet exchanges, or content delivery networks (CDNs).
Dedicated line as an integral part of a leased line
Both leased lines and dedicated lines are point-to-point connections between two interfaces. Leased lines
From the above note, a dedicated line can be a component of a leased line or it can be used in interconnection, for which a leased line does not find application.
Leased line Vs. Dedicated Line: Key Comparisons
Here are the ways in which leased lines compare with Dedicated lines
Comparison Table: Leased Line vs. Dedicated Line
| Factor | Leased line | Dedicated Line |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Point-to-point connection between companies branches (LAN) | Point-to-point connection between ISP & Companies, between companies and Cloud or CDN |
| Bandwidth | Symmetrical bandwidth (equal upload and download speed) | Symmetrical or asymmetrical bandwidth |
| Infrastructure | Relies on service provider infrastructure | May require investment in organization's own network equipment |
| Coverage | Provisioned based on demand, not limited | Flexible deployment based on organization's needs and infrastructure availability |
| Ownership | Owned and operated by the service provider | Depending on arrangement, may be owned by the organization |
| Scalability | Flexible scalability based on requirements and service provider capabilities | Scalability may depend on the capacity of the organization's network equipment |
| Cost | Can be costlier due to leased line provisioning and service level | Generally more cost-effective due to shared infrastructure and flexible options |
| Network Control | Limited control over underlying network configuration and management | More control over network configuration and management |
| Application | Used for interconnecting the LAN of any Enterprises that has branches that is geographically dispersed. | Suitable for various applications, including enterprise connectivity, cloud access, CDN connections, and other specific needs |
| Geographic Flexibility | Geographic limitations based on provider's network coverage | Offers more flexibility in connecting to various locations and service providers |
1. Bandwidth
- Leased Line: Leased lines generally provide symmetrical bandwidth, meaning the upload and download speeds are equal. This ensures balanced and consistent performance for data transmission between locations.
- Dedicated Line: Dedicated lines can also offer symmetrical bandwidth, but they can also be configured to provide asymmetrical bandwidth if required. Asymmetrical bandwidth allows for different upload and download speeds, which can be useful in certain scenarios such as prioritizing download speed for content-heavy applications or services.
2. Infrastructure
- Leased Line: With leased lines, organizations rely on the infrastructure provided by the service provider. They do not have to invest in building and maintaining their own infrastructure.
- Dedicated Line: Dedicated lines may require organizations to invest in their own infrastructure, including the physical network equipment, routers, switches, and cabling.
3. Coverage
- Leased Line: Leased lines are typically available in areas where the service provider has network coverage. The coverage may vary depending on the provider’s infrastructure and geographic reach.
- Dedicated Line: Dedicated lines can be deployed in various locations based on the organization’s needs and infrastructure availability. They are not limited to specific coverage areas
4. Ownership
- Leased Line: Leased lines are owned and operated by the service provider. Organizations lease the line and do not have ownership of the underlying infrastructure.
- Dedicated Line: Dedicated lines can be owned by the organization, depending on the arrangement with the service provider. The organization may have more control over the line’s configuration and management.
Leased line Vs. Dedicated Line: FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions concerning leased line and Dedicated line;
Who owns a leased line?
The service provider owns the leased line infrastructure, while the organization leases and utilizes the line.
What is the exact difference between a leased line and a dedicated line?
A leased line is a general term referring to a connection rented from a service provider, while a dedicated line specifically refers to a connection exclusively used by a single organization.
Is a leased line a dedicated line?
Yes, a leased line can be a dedicated line, providing exclusive use to a single organization.
Is a leased line LAN or WAN?
A leased line can be used to extend a Local Area Network (LAN) or a Wide Area Network (WAN) depending on the organization’s requirements. It is not limited to a specific network type.
Is a dedicated line LAN or WAN?
A dedicated line can be used for both LAN and WAN connections, depending on how it is configured and utilized by the organization. It is not limited to a specific network type.
Conclusion
With what we have covered so far, you have seen that leased lines and Dedicated lines are two technologies used in establishing point-to-point connections between two interfaces.
Leased lines offer dedicated and secure connectivity, ideal for high-bandwidth applications and geographically dispersed locations.
Dedicated lines provide flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and versatility, making them suitable for a range of connectivity needs.
So, depending on your network needs, you already have all the information you need to decide whether to use a leased line or a dedicated line for your connectivity solution.

I am a passionate Networking Associate specializing in Telecommunications.
With a degree in Electronic engineering, I possess a strong understanding of electronic systems and the intricacies of telecommunications networks. I gained practical experience and valuable insights working for a prominent telecommunications company.
Additionally, I hold certifications in networking, which have solidified my expertise in network architecture, protocols, and optimization.
Through my writing skills, I aim to provide accurate and valuable knowledge in the networking field.
Connect with me on social media using the links below for more insights.
You can contact me using [email protected] or connect with me using any of the social media account linked below


