MPLs and DIAs are two networking technologies commonly used in wide area networks and, at times, local area networks.
MPLs is a packet forwarding protocol that uses labels to make forwarding decisions.
DIA on the other hand is a high-speed, secure internet connection provided by an ISP (Internet Service Provider) to an organization.
In this article, we will delve into MPLs vs. DIA, exploring their features, benefits, and how they compare in different scenarios.
What are MPLs?
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a layer 2.5 networking protocol of the OSI model that uses label to enhance the routing and forwarding of data packets across a network.
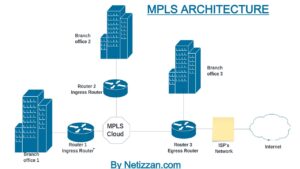
Here is how MPLS work;
When a router in an MPLS circuit receives traffic, it assigns a label to it, which encapsulates the destination IP address to which the traffic is intended. After encapsulation, the router forwards the labeled packet to other switches and routers within the MPLS network. This forwarding occurs at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.
As the labeled packet traverses the MPLS network, subsequent routers utilize the labels to make forwarding decisions rather than relying solely on Layer 3 information. Each router swaps the incoming label with a new label that corresponds to the next hop in the network, enabling efficient packet routing.
Upon reaching the final router before the destination, the last label is removed (popped) to expose the original destination IP address. The router then forwards the packet based on the IP address directly to the intended host. This label removal process occurs at the penultimate hop router, making MPLS operate at Layer 2.5 of the OSI model, as it combines characteristics of both Layer 2 and Layer 3 technologies.
Want more info about MPLS? Read our article on MPLS network architecture.
What is DIA?
Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) is a type of internet connectivity service that provides a direct and dedicated connection from an organization’s network to the internet. Unlike shared internet connections, DIA offers exclusive bandwidth and guarantees consistent performance for the organization.

DIA works by establishing a dedicated physical link between the organization’s network and an Internet Service Provider (ISP). This link can be in the form of a leased line
With DIA, the organization has full control over the dedicated connection and can utilize the entire bandwidth for its internet usage. This direct connectivity allows for faster data transfer, low latency, and consistent network performance.
One of the advantages of DIA is its reliability, as the dedicated connection minimizes the impact of shared network congestion and provides a higher level of service availability compared to traditional internet connections.
Additionally, DIA offers enhanced security features, as the dedicated link reduces the exposure to external threats compared to shared connections.
MPLs vs. DIA: Key Comparisons
Before we go on, it is important to note that MPLs and DIA is not a competing/contradicting technology. It is possible to use both DIA and MPLS in the same network. This post is just an explanation of the two technology and how they compare.
A. Security
Security is a top concern for organizations when it comes to their network infrastructure. MPLS provides inherent security benefits, such as the ability to create virtual private networks (VPNs) and encrypt data traffic.
On the other hand, DIA’s direct internet connection raises some security considerations. It exposes network endpoints directly to the internet. Organizations must implement good security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to mitigate potential risks.
B. Speed
Network speed directly impacts user experience and productivity. MPLS networks offer dedicated bandwidth, ensuring reliable and consistent performance. However, MPLS may not always provide the fastest speeds due to the nature of its infrastructure.
In contrast, DIA’s direct connection to the internet can offer high-speed connectivity, especially for cloud-based applications and internet-dependent operations.
C. Direct connection
DIA’s direct connection to the internet offers advantages in terms of reduced latency and enhanced cloud application performance. By bypassing MPLS infrastructure, organizations can achieve faster access to cloud resources and services.
However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks, such as security concerns and the need for robust internet connectivity and redundancy.
D. Capacity Comparison
MPLS networks typically offer high capacity and can handle large volumes of data traffic. However, scaling MPLS networks can be a complex and time-consuming process.
On the hand, DIA can provide scalability and flexibility by leveraging the organization’s existing internet connection. The ability to rapidly scale bandwidth according to evolving needs makes DIA an attractive option for organizations experiencing significant growth or dynamic network requirements.
E. Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS ensures the prioritization of critical applications and services over the network. MPLS networks excel in providing robust QoS capabilities. This allows organizations to prioritize traffic based on specific requirements.
DIA, on the other hand, may have limitations in QoS management due to its reliance on the public internet. Though, advancements in traffic management technologies and the implementation of quality monitoring systems can mitigate these limitations in DIA.
F. Network Layer Comparison
As explained before, MPLs is layer 2.5 networking protocol that uses label to enhance the routing and forwarding of data packets across a network while DIA operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model
G. Coverage Comparison
Network coverage is a crucial consideration, particularly for organizations with geographically dispersed locations. MPLS networks often have widespread coverage, allowing seamless communication between branches. MPLS is mainly used in wide-area networks.
DIA, on the other hand, can be used to provision internet service to a local area network, a wide area network, a metropolitan area network, and other network coverages.
H. Historical Perspective: DIA vs. MPLS
Understanding the historical timeline and adoption trends of MPLS and DIA provides valuable insights into their evolution and popularity.
MPLS has been a widely adopted technology for many years, offering reliable connectivity and QoS capabilities.
DIA, on the other hand, has gained prominence in recent years due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and the increasing demand for direct internet connectivity. Organizations have chosen either option based on their specific requirements and priorities.
What is the alternative to MPLS?
In addition to comparing MPLS and DIA, it’s important to explore alternative solutions that can address the limitations of both technologies.
SDWAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is the best alternative to MPLs, it offers enhanced security, flexibility, and efficient traffic management.
SDWAN leverages multiple network connections, including MPLS and DIA, to optimize network performance and achieve cost savings. It provides centralized management and control. This helps organizations to dynamically route traffic based on application requirements and network conditions.
The Downside of MPLS
While MPLS has been a reliable choice for many organizations, it’s essential to understand its limitations. Expensiveness is the major limitation of this network technology. So any business looking for a cost-effective service may not be able to afford it.
Additionally, MPLS networks are static and closed, which can pose challenges when onboarding new SaaS services or incorporating dynamic cloud-based applications. Long-term provisioning for MPLS connections can be time-consuming, often taking up to three months to establish connectivity to a branch.
MPLs vs. DIA: FAQs
Here are some of the frequently asked questions on how DIA compare with MPLS;
What is the difference between DIA and MPLS?
DIA (Direct Internet Access) provides direct connectivity to the internet, while MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) is a private network technology that offers secure and efficient data transfer between multiple locations.
What are the primary advantages of DIA?
DIA provides direct and fast access to the internet, enabling organizations to leverage cloud services, access global resources, and support high-bandwidth applications. It offers flexibility, scalability, and can be a cost-effective solution for internet connectivity
What are the primary advantages of MPLS?
MPLS offers secure and reliable connectivity between multiple locations, ensuring data privacy and efficient data transfer. It provides traffic engineering, QoS features, and is ideal for applications that require low latency, minimal jitter, and high network performance.
Can I combine DIA and MPLS in my network?
Yes, it is possible to combine DIA and MPLS in a network setup. Organizations can use DIA for internet access and MPLS for secure interoffice connectivity, leveraging the strengths of each technology based on specific requirements.
When should I consider using MPLS instead of DIA?
MPLS is often preferred when organizations require secure, reliable, and predictable connectivity between multiple locations. It offers better control over network traffic, enhanced QoS capabilities, and is well-suited for mission-critical applications or data transfers between geographically dispersed sites.
When should I consider using DIA instead of MPLS?
DIA is typically suitable when organizations prioritize direct internet access, require high-speed connectivity, and need flexibility in accessing various internet resources. It is often cost-effective for organizations with limited interoffice data transfer requirements.
What factors should I consider when choosing between DIA & MPLS for my organization?
Factors to consider include the organization’s connectivity needs, security requirements, budget constraints, geographic distribution of sites, desired network performance, and reliance on cloud services.
Conclusion
From what we have covered so far, you must have learnt that MPLS excels in security, QoS, coverage and network layer functionality. It offers reliable and controlled connectivity.
DIA on the other hand provides cost-effective scalability, high-speed internet access, and enhanced cloud application performance. Depending on specific requirements such as security, speed, scalability, and budget constraints, you can choose between MPLS and DIA.
For organizations seeking a more flexible and dynamic network architecture, SDWAN is the recommended option. SDWAN combines the strengths of MPLS and DIA, offering centralized management, enhanced security, and efficient traffic routing capabilities. It provides organizations with the flexibility to leverage multiple network connections and adapt to evolving network needs.

I am a passionate Networking Associate specializing in Telecommunications.
With a degree in Electronic engineering, I possess a strong understanding of electronic systems and the intricacies of telecommunications networks. I gained practical experience and valuable insights working for a prominent telecommunications company.
Additionally, I hold certifications in networking, which have solidified my expertise in network architecture, protocols, and optimization.
Through my writing skills, I aim to provide accurate and valuable knowledge in the networking field.
Connect with me on social media using the links below for more insights.
You can contact me using [email protected] or connect with me using any of the social media account linked below



