MPLS and Internet are two confusing networking concepts.
MPLS is a packet forwarding algorithm that uses labels to make a forwarding decision.
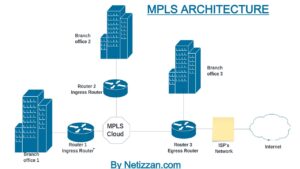
Recommended: MPLS network architecture
Internet, on the other hand, is a global network that interconnects Different WAN, LANs, or even end host devices.
In this article, we will delve into MPLS Vs. internet, highlighting how they compare in different scenario.
MPLS Vs. Internet: 9 Key Differences
Here are some of the ways in which MPLS differs from internet;
- MPLS is a packet forwarding algorithm that uses labels to make forwarding decisions, while the Internet is an infrastructure that interconnects different WAN, LAN, or end-host devices.
- MPLS is a traffic distribution technology, while the Internet is the infrastructure on which traffic is distributed. This means MPLS can operates on Internet infrastructure.
- Network Layer: MPLS uses layer 2.5 of the OSI model to operate, while the internet is an infrastructure that have packet forwarding technology that operates in layer 2, layer 3 or even layer 2.5 of the OSI model.
- Coverage: MPLs is normally implemented on Wide Are network which has lower network coverage than the internet.
- Packet forwarding mechanism: Traffic forwarding on the internet is based on IP routing protocols, which use IP addresses to make forwarding decisions, but MPLS, on the other hand, uses label to make forwarding decisions. Read: MPLS Vs. IP routing.
- Traffic Control: MPLS incorporates a unique traffic engineering feature, and this makes it different from most packet forwarding technologies used on the Internet. Traffic engineering allows prioritization of certain types of traffic.
- Security: MPLS generally offers a more secure network environment compared to many routing algorithms utilized on the Internet.
- Cost: MPLS is cost intensive because of the new hardware infrastructure needed to implement it while the routing protocols found on the internet mainly uses existing infrastructure.
- Speed: MPLS typically delivers high-speed network performance by using label; a Layer 2 information, to make forwarding decisions. This eliminates delays associated with IP lookups
FAQ on MPLS vs. Internet:
Here are some frequently asked questions on MPLS vs. Internet:
Can MPLS & the Internet be used in the same network?
Yes, MPLS is a packet forwarding technology that can indeed be implemented on the existing Internet infrastructure.
What is the primary purpose of MPLS?
MPLS is primarily used to enhance traffic flow, provide Quality of Service (QoS) features, and optimize data routing within a network or across different locations of an organization.
How does MPLS differ from traditional Internet routing?
MPLS employs label-based forwarding technology, where packets are assigned labels for efficient routing decisions, while traditional internet routing uses IP addresses to make forwarding decisions. Read: MPLS Vs. IP routing.
How does security differ between MPLS and the Internet?
MPLS, being used within private networks, provides a level of security, keeping traffic within the organization’s boundaries. The Internet, being public, require additional security measures like encryption or VPNs.
Does MPLS go over the Internet?
No, MPLS operates within private networks and does not utilize the public Internet for data transmission.
Is MPLS more secure than SD-WAN?
MPLS is generally considered more secure than SD-WAN due to its private network nature, while SD-WAN operates over public networks like the Internet, which may require additional security measures.

I am a passionate Networking Associate specializing in Telecommunications.
With a degree in Electronic engineering, I possess a strong understanding of electronic systems and the intricacies of telecommunications networks. I gained practical experience and valuable insights working for a prominent telecommunications company.
Additionally, I hold certifications in networking, which have solidified my expertise in network architecture, protocols, and optimization.
Through my writing skills, I aim to provide accurate and valuable knowledge in the networking field.
Connect with me on social media using the links below for more insights.
You can contact me using [email protected] or connect with me using any of the social media account linked below



